DFC - Dedicated Freight Corridor - A Game changer
Source: DFCCIL
DFC Video Link
Hqrs: New Delhi
2006 October - Incorporation of DFCCIL (Schedule”A”) Government Company, as SPV – Special Purpose Vehicle, is a wholly owned company of the Ministry of Railways registered under Company Act 1956.
· · Estimated Project Cost - Rs. 82,000 Crores (Approx)
· The Eastern & western dedicated freight corridors entail an investment of 12 billion dollars,
· Eastern Corridor - World Bank Loan of 1.86 Billion dollars (Rs. 13000 Crores)
· Western Corridor - JICA (Japanese International Cooperation Agency) loan of 5.2 Billion Dollars (Rs. 37000 Crores)
· The balance between Project Cost and Loan is borne by Govt of India through Equity.
Need of DFC
· Eastern Corridor ( EDFC ) from Ludhiana ( Punjab ) to Dankuni (Near Kolkata)
· Western Corridor (WDFC) from Jawaharlal Nehru Port, Mumbai to Dadri
near Delhi.
· The Delhi-Mumbai rail route and the Delhi –Howrah rail route are highly congested at present.
· IR has lost a significant portion of its Freight business to the Road sector and has planned to recover the market share through DFC.
Beginning:
· Golden quadrilateral connecting 4 Metropolitan cities of Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata and its diagonals 1. Delhi to Chennai and 2. Mumbai to Kolkata – Total route length of 10,000 Kms –
Share of Golden quadrilateral at present
Route | Passenger traffic | Freight traffic |
16 % | 52 % | 58 % |
· Line capacity varying between 120 % to 150 % in Eastern Corridor (Delhi to Kolkata) and in Western Corridor (Delhi to Mumbai) – Highly saturated
· IR lost its share in freight traffic from 83 % in 1950-51 to 30 % in 2018-19
· To meet the growth of Indian Economy in recent decades and to garner the share of Freight transport, the Govt mooted the conception of Dedicated Freight Corridors
· Beginning step in the above direction is the Presentation of Railway Budget in 2005-06.
· 2006 – A SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle) named Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India limited was incorporated as a company under the Companies Act, 1956/2013.
Mission:
· To build a Corridor with appropriate technology
· To regain market share of Freight transport
· To set up Multimodal logistic parks along the DFC to provide complete solution to customers
· To adopt the Railways as the most environmental friendly transport mode
Salient Features
· Chairman : De facto Chairman, Railway Board
· Hqrs: New Delhi
· Total route length : 3360 kms
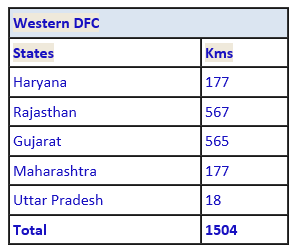
· Western Corridor : 1504 Kms From Dadri (UP) to JNPT -Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Mumbai)
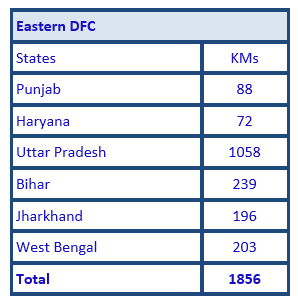
· Eastern Corridor : 1856 Kms From Ludhiana(Punjab) to Dankuni (West Bengal)
· The Railway’s share expected to go up from the present level 30 % to 45% in the Total transport sector
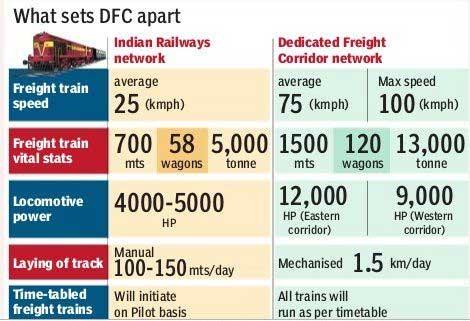
· It is exclusively for Freight trains. So it should be possible to run time-tabled trains with guaranteed transit time.
· Last mile connectivity – by tying up with truck operators. So that offered door to door services to the Customers.
· Setting up of Multimodal logistics parks along the Corridor to facilitate all kinds of value addition from packaging. Retailing, labelling, pelletizing etc.
· Design-Build Lump-sum Contract strategy – Construction of DFC. Being a design build contract bidder is supposed to quote lump-sum contract price for the total work including design, construction, testing, commissioning and liability during defect liability period. It is akin to EPC Projects. Click for Article on EPC in the blog.
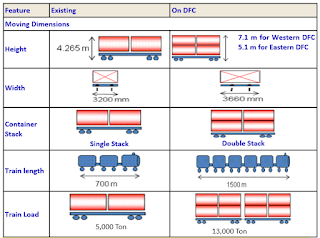
· Western corridor will cater double stack containers on electrified traction, which is first in the world
· RO-RO – Roll On Roll Off traffic – Western Corridor - to attract non-bulk traffic particularly at short lead to avoid cost of transhipment
Latest update on May 2022
EDFC - 1875 RKM From Ludhiana (Punjab) to Dankuni (West Bengal) covering Punjab, Haryana, UP, Bihar, and Jharkhand, West Bengal.
WDFC - 1506 RKM. From Dadri (UP) to Jawaharlal Nehru Port (Mumbai) covering UP, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
Key points for MCQ
DFCCIL stands for Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited
Western DFC - From Dadri (UP) to JN Port (Mumbai)
EDFC - From Ludhiana (Punjab) to Dankuni (West Bengal)
WDFC - 1506 RKM
EDFC - 1875 RKM
RKM stands for Route Kilo Meters
DFCCIL Hqrs - New Delhi
Total Cost - Rs. 1,24,000 Crores
Relationship with Indian Railways:
· Concessioner is Indian Railways and Concessionaire is DFCCIL
· Period is 30 years (from commencement of operations)
· Accept freight trains on its track on payment of user charge called TAC – Track Access Charge by Indian Railways and other Private Train operators.
· Land will be acquired by IR under Railway Amendment Act, 2008 and leased to DFCCIL
· Financing the Project: Loan from External bilateral/ Multilateral funds recd via Ministry of Railways and equity contribution from the Ministry of Railways.
· Main source of Revenue to DFCCIL is TAC – Track Access Charge
· TAC consists of Fixed and Variable components. Variable component based on volume of traffic in terms of 000 GTKMs
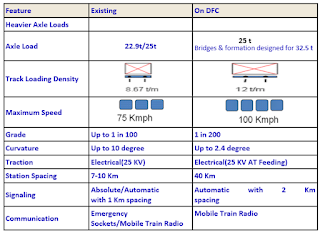
· Cost of construction of Double Line electrified Track – Rs. 18 Crores Per KM (in IR , it is Rs.12 Crores per KM). The reasons for increasing cost are
A. Electric traction of 2 x25 KV, 58hz single phase AC
B. Double line automatic signaling
C. Standard of loading of 32.5 Tonnes Axle Load
D. Will have grade separation from IR. Existing lines in the form of flyovers to ensure free flow of trains on both the systems.
Advantages:
1. Bring about a paradigm shift in Freight operations
2. Reduction in the unit cost of transportation.
3. Higher speeds
4. Better turnaround of Wagons
5. Act as Catalyst for the Development of Industry and Areas along the Corridor.
6. Increased payload to tare ratio (by higher axle load wagons)
7. Improved SEC - Specific Energy Consumption
8. Ultimate objective is to reduce the O & M Costs (Operation & Maintenance)
9. DFC will save more than 450 million ton of CO2 in first 30 years of operation.
· Coming up Freight Corridors are
. 
*****
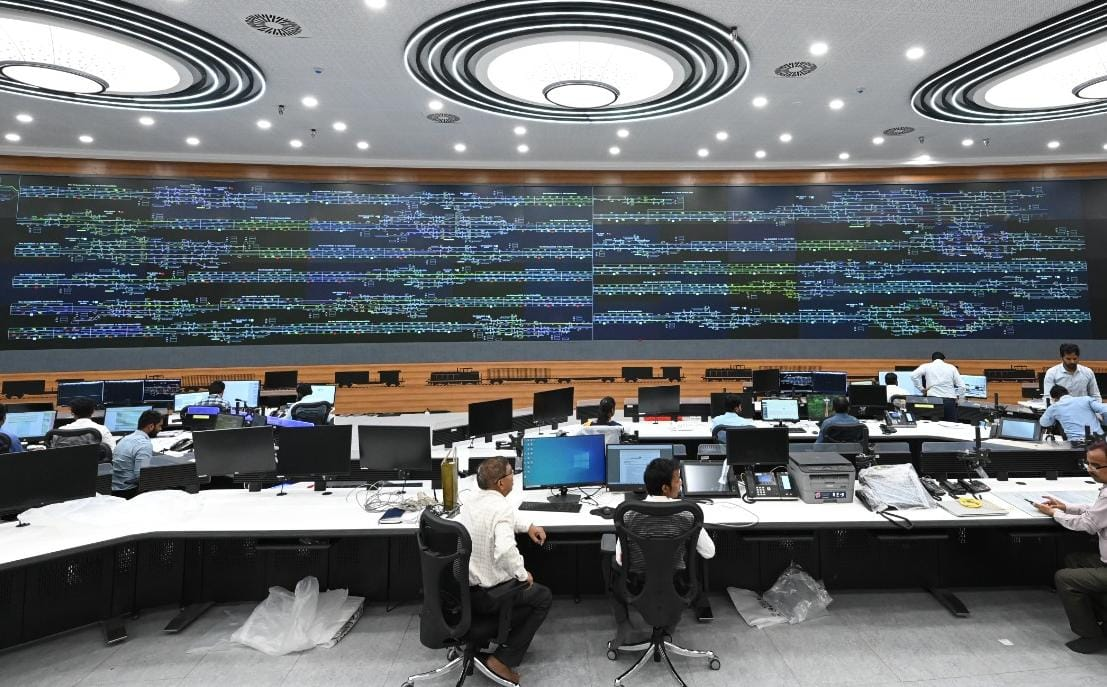

OCC - Operation Control Centre
WDFC
At Ahmedabad
Operationalised in March 2023
Controls entire WDFC’s Train operations, Signalling, and Power Supply and monitor the health of Rolling Stock & Track Safety.
It is equipped with advanced technologies and new applications for Train operations.
SCADA - Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition operations
TPC - Traction Power Controller operations will be done from the OCC
Nerve-centre of WDFC - 1506 KMs - Double Track Electrified 2 x 25 KV From Mumbai JNPT (Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust) to Dadri via Vadodara, Ahmedabad & Rewari, covering the States of Haryana, UP, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra.
Green Building
Serve the Round-the-Clock
EDFC
Going to be a launch
OCC - for EDFC - Prayagraj, UP - World’s Second Largest OCC
Command Centre for the entire route length of 1856 KMs of EDFC
Green Building rating of GRIHA4 - equipped with Solar power and rainwater harvesting
1560 Sq Meter with a video wall of more than 90 metres.
The Divyang-friendly one
Modern interiors, Best-in-class acoustics, ergonomically designed to suit the needs of the Traffic Controllers
Integrated SCADA with TMS (Train Management System) - will enable the Traction Controllers to monitor, control as well as remotely operate power supply equipment at Traction Sub Stations, Sectioning and Parallelling posts for the Entire Network.
Under the Make in India or Atma Nirbhar initiative, the system has been developed by Alstom, and supported by their design teams in Bangalore.
EDFC - 1875 KMs - Two distinct segments:
Double Track - 1409 KMs - Dankuni to Khurja
Single Track - 447 KMs - Khurja to Dadri
DFCCIL Network
State | WDFC | EDFC | Total | % Share |
UP | 19 | 1078 | 1097 | 32 |
Rajasthan | 567 | - | 567 | 16 |
Gujarat | 565 | - | 565 | 16 |
Haryana | 177 | 72 | 249 | 7 |
Bihar | - | 239 | 239 | 7 |
West Bengal | - | 203 | 203 | 7 |
Jharkhand | - | 195 | 195 | 6 |
Maharashtra | 178 | - | 178 | 6 |
Punjab | - | 88 | 88 | 3 |
Total | 1506 | 1875 | 3381 | 100 |
Key Points for MCQ
DFCCIL stands for Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Limited
OCC stands for Operations Control Centre
OCC - WDFC - Ahmedabad
OCC - EDFC - Prayagraj
OCC at Prayagraj - going to be launch - World’s Second Largest one
OCC at Ahmedabad - Operationalised in March 2023
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition
DFCCIL - 3381 KMs
WDFC - 1506 KMs
EDFC - 1875 KMs
UP covers - Highest Network of DFCCIL - 32 %
DFCCIL - Incorporated - in 2006 - as a Schedule A Company under the Companies Act, 1956
MCQ on DFCCIL
1. Headquarters of DFCCIL
Answer 1: Mumbai
Answer 2: Kolkata
Answer 3: New Delhi
Answer 4: Bangalore
2. DFCCIL is a ______
Answer 1: Registered Company
Answer 2: Government Organisation
Answer 3: Private company
Answer 4: subsidiary of World Bank
3. Target for completion of Dedicated Freight Corridor
Answer 1: 2022 December
Answer 2: 2021 December
Answer 3: 2023 June
Answer 4: 2024 December
4. Estimated project cost (approx) of DFC
Answer 1: 1.24 lakh crore
Answer 2: 2.24 lakh crore
Answer 3: 3.24 lakh crore
Answer 4: 4.24 lakh crore
5. DFC project cost financed by _________
Answer 1: World Bank & LIC
Answer 2: JICA & LIC
Answer 3: World Bank and JICA
Answer 4: World Bank, JICA & Asian Development Bank
6. IR lost its share in freight traffic from ___ in 1950-51 to ____in 2018-19
Answer 1: 83 % , 30 %
Answer 2: 95 % , 55 %
Answer 3: 83 % , 53 %
Answer 4: 63 % , 30 %
7. TAC stands for _______ (DFCCIL)
Answer 1: Travelling Access Charge
Answer 2: Track Access Component
Answer 3: Track Access Charge
Answer 4: Track Activation Charge
8. DFCCIL established in the year
Answer 1: 2006
Answer 2: 2016
Answer 3: 2010
Answer 4: 2012
9. Chairman of DFCCIL is
Answer 1: Prime minister
Answer 2: Railway Minister
Answer 3: Member/Finance
Answer 4: CEO & Chairman, Railway Board
10. Dedicated Freight Corridor is meant for
Answer 1: Passenger trains and Freight Trains
Answer 2: Exclusive for Freight Trains
Answer 3: Exclusive for Passenger Trains
Answer 4: Priority for Freight Trains. But can allow Passenger Trains
Answers;
3
1
3
1
4
1
3
1
4
2
%%%


