Designed to help the candidates appearing the Appendix 3, LDCE, 70% etc of Railway Accounts
Thursday, August 27, 2020
eRA - Electronic Reverse Auction in Indian Railways
What is eRA - Electronic Reverse Auction in Indian
Railways
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
Auction (Forward Auction) |
a public sale in which goods are sold to the highest bidder . One seller, but many buyers. Example is Scrap Sales in IR through
E-Auction |
|
|
|
|
|
R |
A |
Reverse Auction |
A
public Procurement in which goods are brought from the lowest bidder. One buyer, but many sellers. |
|
|
|
|
e |
R |
A |
Electronic Reverse Auction |
An
online, real-time dynamic Reverse Auction. (in IR - through IREPS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive article
on eRA - will be posted shortly
Wednesday, August 19, 2020
LDCE Written exam results, 2020 year - Accounts Dept of SCR
Tuesday, August 18, 2020
M&P Programme (Machinery & Plant)
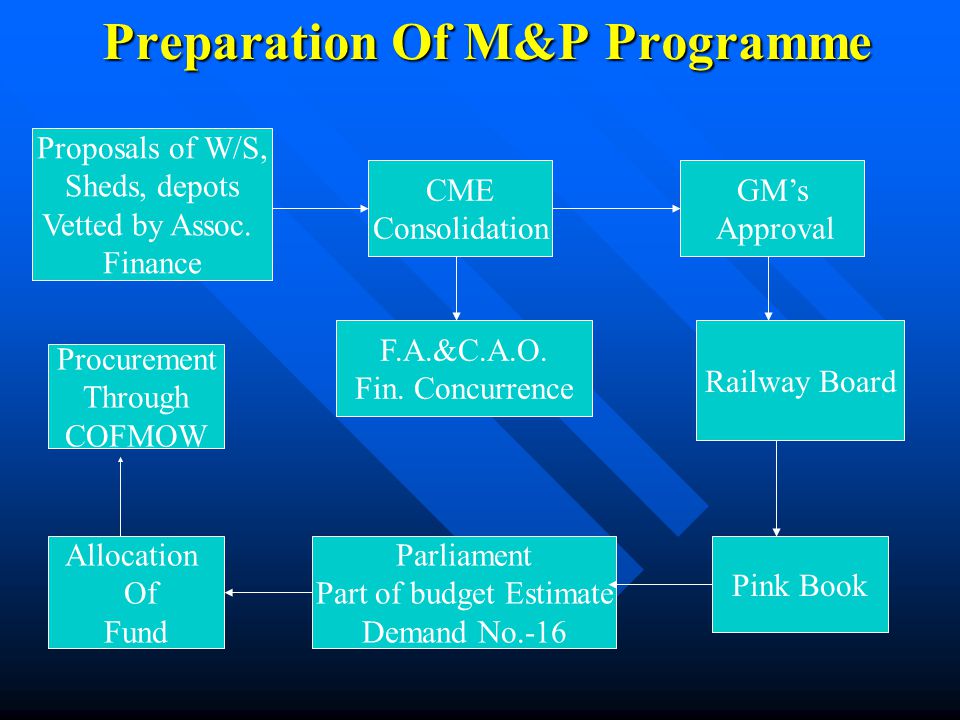
M&P Programme
Source: 10th Chapter of Rolling Stock Code Click for Rolling Stock Code
·
Investment decisions relating to
the creation, acquisition and replacement of assets on the Railways are
processed through the 3 different Programs
· They are
1. Rolling Stock Program (Plan Head 21)
2. M & P Program (Plan Head 41 )
3. Works Program (Rest of the
Plan Heads)
·
Click for article on Works Program
·
Click for article on Rolling Stock
Program
·
Plan
Head 41 - covers M&P items (under RB
& GM powers)
·
2020-21
M&P Grant - Rs. 487 Crores
·
Nodal
Officer - PCME (for budget allotments
& utilization of funds). He
is nodal officer for distribution of Ceiling (preliminary M&P Programme)
among various depts. The overall ceiling
should, however, be followed strictly.
·
Machinery and Plants are expensive
assets both to acquire and maintain.
Hence, it is important that investments in M&P shall be made
thoughtfully.
·
Items proposed under GM’s Out of
turn sanctions should not be included in the regular M&P Programme for
Board’s sanction.
·
The monetary limits for submission
of preliminary M&P proposals to Railway Board are revised from time to
time.
M&P Portal
·
Website address: http://www.irmnp.com/
·
Developed to allow easy creation
and processing of M&P proposals by users on Indian Railways.
Salient features of Portal
1. Can create proposals in
minutes and refine them as needed.
2. Users can stay ahead of all the deadlines.
3. Submit the proposals electronically to Zonal Hqrs and Railway
Board within no time.
4. Can track the sanction of
proposals issued by the Railway Board.
5. Tracking the status of procurement (by COFMOW)
6. Submit information about WIP - Works in Progress and receive funds
accordingly.
7. Keep the Asset Register updated automatically.
8. User ID and Password of
users by CME(Planning) of Zonal Railway/PU.
Preliminary M&P Program
·
Items included are (Figures may vary from time to time. Please
check latest amendments to Model SOP)
ü Rs. 50 lakhs above - each item
ü Rs. 30 lakhs above - each
item (Electronic in motion weigh bridges)
ü All Road vehicles irrespective of cost (Exception is sanctioning
of procurement of two wheelers under M&P– under GMs powers)
·
Submit consolidated Preliminary
M&P Programme through M&P Portal
maintained by Railway Board.
·
Estimated costs of the machines
indicated in the proposals should be present day realistic costs and should
include cost of essential accessories.
·
The present day cost - adopt from
1. The latest compendium issued by COFMOW 2. M&P Portal
·
Costs for other machines may be
obtained through market surveys.
·
Preliminary M &P Due Date: September / October month of every year or
date specified by the Railway Board.
After which, the portal would disallow any subsequent submissions.
·
Final M&P Due Date - Discussed
with the Railways by the Railway Board during December or January of every year
End-loaded
expenditure :
·
In other works, there is steady
outflow of cash as the project advances, and the trend of expenditure is
uniform.
·
But, in case of M&P
procurements the booking starts only after a machine is dispatched and hence
the expenditure is end- loaded.
·
With an average lead time of 3
years, the value of W.I.P items is often therefore more than 3 times the budget
sanctions.
Difference between M&P and T&P
M&P -
Machinery & Plant covers:
ü A machine that remains stationary and immovable.
ü That means job comes to machine and not vice versa.
ü All vehicles such as staff cars, Lorries, Diesel utility vehicles,
Road mobile Cranes, Front end loader/JCB cranes & Fork lifts.
T&P - Tools & Plant covers:
ü All movable machines like pneumatic drills, power saws, tools
& plants such as jigs and fixtures.
ü Small tools and equipments required for maintenance of machines
ü All measuring instruments / Gauges (irrespective of their unit
cost)
ü Upkeep of office such as
furniture, computers, printers etc.
ü Limit for Tools and Plant -
Up to Rs. 10 Lakhs each - Charged to Revenue.
If it is Rs. above Rs. 10 lakhs, procurement of such T&P is
processed under M&P.
Codal
life:
· Subject to modification from time to time as amended in Accounts
Code.
· It is merely an average economic life, assumed for the specific
purpose of making long term planning for replacements.
· Normally condemnation should be on age and condition basis.
· Condition basis arrived by derivative/derived of hours usage
(double or single shift), load factor, maintenance standards etc.
Annexure 10.2
of Chapter 10 of Rolling stock code.
|
S.No |
Codal life of machines |
Average Life in Yrs |
|
1. |
Machine Tools like Lathes,
Planners, Drilling, Boring and Milling machines etc. |
15 |
|
2. |
High Precision and special
purpose machine like wheel lathes etc. |
15 |
|
3. |
Tool Room and Testing Laboratory
equipment |
15 |
|
4. |
Foundry and Forge Equipment |
15 |
|
5. |
Heat Treatment Equipment |
15 |
|
6. |
Cranes – E.O.T |
25 |
|
7. |
Power Generation Machinery &
Switches |
15 |
|
8. |
General purpose light machinery
e.g. band saws, floor grinder etc. |
10 |
|
9. |
Air compressor |
15 |
|
10. |
Miscellaneous machines e.g.
light cleaning machines, test equipment in diesel sheds, workshops, depots
and sick lines |
15 |
|
11. |
Construction Machinery |
15 |
|
12. |
Track Maintenance equipment |
20 |
|
13. |
Station machinery e.g. weighing
machines etc. |
15 |
|
14. |
Miscellaneous machinery and
equipment for hospital, offices etc. |
10 |
|
15. |
Mechanical Weigh Bridges |
15 |
|
16. |
Electronic-In-Motion Weigh
Bridges |
08 |
|
17. |
Diesel Pumps |
10 |
|
18. |
Welding equipment including
diesel welding sets |
10 |
|
19. |
Diesel refrigeration equipment |
15 |
|
20. |
Material handling equipment like
FLT, Lister trucks etc., |
10 |
|
21. |
Traversers |
25 |
|
22. |
Fuel station dispensation
equipment |
10 |
|
23. |
Bulldozers and other earth
moving equipment |
15 |
|
24. |
Motor Boats |
10 |
|
25. |
Hydraulic re-railing equipment |
15 |
|
26. |
Staff cars including Jeeps |
07 |
|
27. |
Light Motor vehicles |
10 |
|
28. |
Heavy Motor vehicles |
10 |
|
29. |
Tractors |
10 |
Creation of new assets on Additional account
·
Proposals should be supported with Financial
justification and Rate of Return (10%) (Chargeable to Capital)
·
Vetted by Associate finance
·
Vetting is not required for machines required on
safety considerations such as medical/safety
equipment for ART/ARME (chargeable to DF IV)
·
Other particulars such as Reduction in cycle time,
improved quality and reliability, reduction in monotony etc should indicate in
the proposal.
Replacement
proposals:
·
Chargeable to DRF
·
Proposing one-to-one replacements
should be avoided, unless
·
The requirements of the proposer
have remained unchanged since the original equipment was acquired and
·
Machines of higher productivity
and reliability cannot be economically justified.
The following
details - spelt out in the replacement proposal:
1.
Codal life of the machine and
actual years worked along with the number of shifts per day.
2.
Jobs undertaken and the workload
for the machine.
3.
If reconditioning of the existing
machine or outsourcing was considered and the outcome.
4.
Total number of similar machines
in the load-centre and shortfall in capacity.
5.
Economics of acquiring one or two
machines to replace a larger set.
6.
Replacement proposed should be
substantially for same function and differences, if any, should be clearly
brought out with reasons.
7.
The cost of replacement may be
compared with original equipment and reason for any abnormal increase
explained.
8.
Proposals for Road vehicles should
accompany survey committee report comprising the condition of the vehicle,
expenditure incurred, mileage and recommendation.
9.
Reconditioning or Replacement: There
are situations where partial/ full reconditioning of machine is financially
more viable in comparison to its condemnation and replacement.
Master Plan:
·
For utilization of space &
Layout in Workshops/Repair Sheds.
·
Every Workshop or Repair Shed should
have a Master Plan pinpointing locations of the machine to be procured in
additional / replacement account in future.
·
So that, as and when new machines
are acquired, these should straight away get installed according to this master
plan.
·
Critical review of 20 Years and
above Machines and Over aged machines
incl: Cranes for their continued retention, so that floor space is effectively utilized. Retaining them only after a clear
certification of the in charge Officer duly certifying the sufficient load
exists for the same.
Works in Progress (WIP) Statement
·
Sanctioned and for which vetted
indents are submitted, but not completed or closed.
·
Should state the status of
procurement.
·
In absence of any clear indication
of procurement, funds should not be allotted.
·
Due date: 15th December every
year.
·
Funds projection - through M&P Portal maintained by
Railway Board.
Summary
- Top of the WIP Statement
1.
Costing Rs. 2.5 Crores and above each
2.
Costing below Rs. 2.5 Crores each
3.
Sanctioned under GM's Powers ( However list of items need not be sent to
Railway Board)
Budgeting
:
·
Validity of Sanction - 5 Years
- sanctioned under M&P
·
Validity of Sanction - 3 years
- Sanctioned under GM's OOT powers
·
Above 2.5 Crores each itemised in
Pink Book with Pink book number, allocation wise breakup separately
·
Allotment of M&P items - Less
than 2.5 Crores each and sanctioned under GM's OOT powers - distribution by the Nodal Officer
i.e., PCME and itemised in the LAW -
List of Approved Works with a unique LAW number.
Four Categories - M&Ps
Category
A
·
Sophisticated and unique machines
requiring extensive market survey
·
Specialized knowledge of the World
of machine tools.
·
Procured by COFMOW only.
Category
B
·
Machines like EOT cranes, welding
machines, compressors, Road Mobile Cranes, Diesel Gensets etc., that figure
frequently in the M&P Programs
·
Carefully procured, duly
eliminating unreliable vendors from a highly competitive market
·
Requirements
from Zonal Rlys are in bulk.
·
Entering into Running / Rate
contracts for 2 to 3 years with price variation clause
·
Consider ILM option - Install, Maintain & Lease like construction companies hire cranes on
long term basis
·
Procured by COFMOW only.
Category
C
·
Special machines of unique and
sophisticated nature for which domain knowledge may not exist with COFMOW
·
Requirements
are not in bulk
·
Procured by Zonal Railways but
after seeking dispensation from COFMOW well in time.
Category
D
·
Other machines of smaller value
below a certain limit barring certain excluded items, as stipulated by RB.
·
Medical equipment whose
procurement is best left to the user Railway.
Notes:
1.
M&P items costing up to Rs. 30
Lakhs each can be procured by Zonal Railways/Production units on their own,
without seeking dispensation from COFMOW subject to the exception list issued
by COFMOW and items covered under Rate contracts of COFMOW.
2.
Medical items equipments can be
procured by Zonal Railways/Production units.
Budgetary
Reviews:
·
PCME is Nodal Officer - He/She
will critically review these projections recd from Depts and submit to PFA duly
giving the reasons for allocation wise variations with the Budget Grant during
the budgetary stages.
Asset
Register of M&P:
·
On procurement, a unified 9 digit
code number to be allotted for each machine.
·
On successful commissioning of a
new machine, it is included in teh Asset register with all the details.
·
No machine shall be kept in
service without Unified Code Number, which is prominently painted on it for
easy identification.
·
On disposal (condemnation) or
transferred to Other Railway, the same is removed from the Asset Register of
Parent Railway.
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
Unit |
Sub
Location |
Machine
Group |
Individual
machine No. |
|||||
|
ICF/Division |
Shop
like Machine shop |
Wheel
Lathe, Cranes etc |
|
|||||
Likely
Descriptive Questions
1. Essay question on M&P Progrramme
2. Short Notes questions on A. Differences between M&P and
T&P B. Master Plan C. M&P Portal D. Asset Register of M&P
Material for MCQs - Multiple
Choice Questions
1. Nodal Officer for M&P Programme in Zonal Railway - PCME
2. Validity for RB Sanctions -
5 years
3. Validity for GM Sanctions - 3 years (OOT - Out Of Turn)
4. Unified code - 9 digits
5. Categories of M&Ps - for M&P Programme - 4
6. Dispensation of COFMOW not required - up to Rs. 30 Lakhs
7. Plan Head for M&P - 41
8. GM's Powers - M&P - up
to Rs. 50 Lakhs
9. GM's Powers - Electronic Weighing Machine - Up to Rs.30 Lakhs
10.
Sanctioning of Two Wheeler for RPF
post - by GM
11.
T&P item up to Rs. 10 Lakhs -
Charged to Revenue
12.
T&P item - Rs. 10 Lakhs and
above processed as M&P and charged to erstwhile Demand No.16 (DRF/CAP/DF)
13.
Medical equipments - of any cost -
Procured by Zonal Raiways
14.
Rs. 2.5 Crores and above -
itemised in Pink Book
15.
Below Rs. 2.5 Crores - included in
the LAW - List of Approved Works
16.
LAW Full form - List of Approved
Works
17.
WIP Full form - Works In Progress
18.
With an average lead time of 3
years, the value of W.I.P items is often therefore more than 3 times the budget
sanctions.
19.
All Road vehicles Proposals
irrespective of its cost to be included in the M&P Programme (except Two
Wheelers, which can be sanctioned by GM)
20.
Vetting of Associate finance is required
for all M&P Proposals of New Assets on Additional Account (Except for
Safety and Medical equipments - charged to DF)
******



